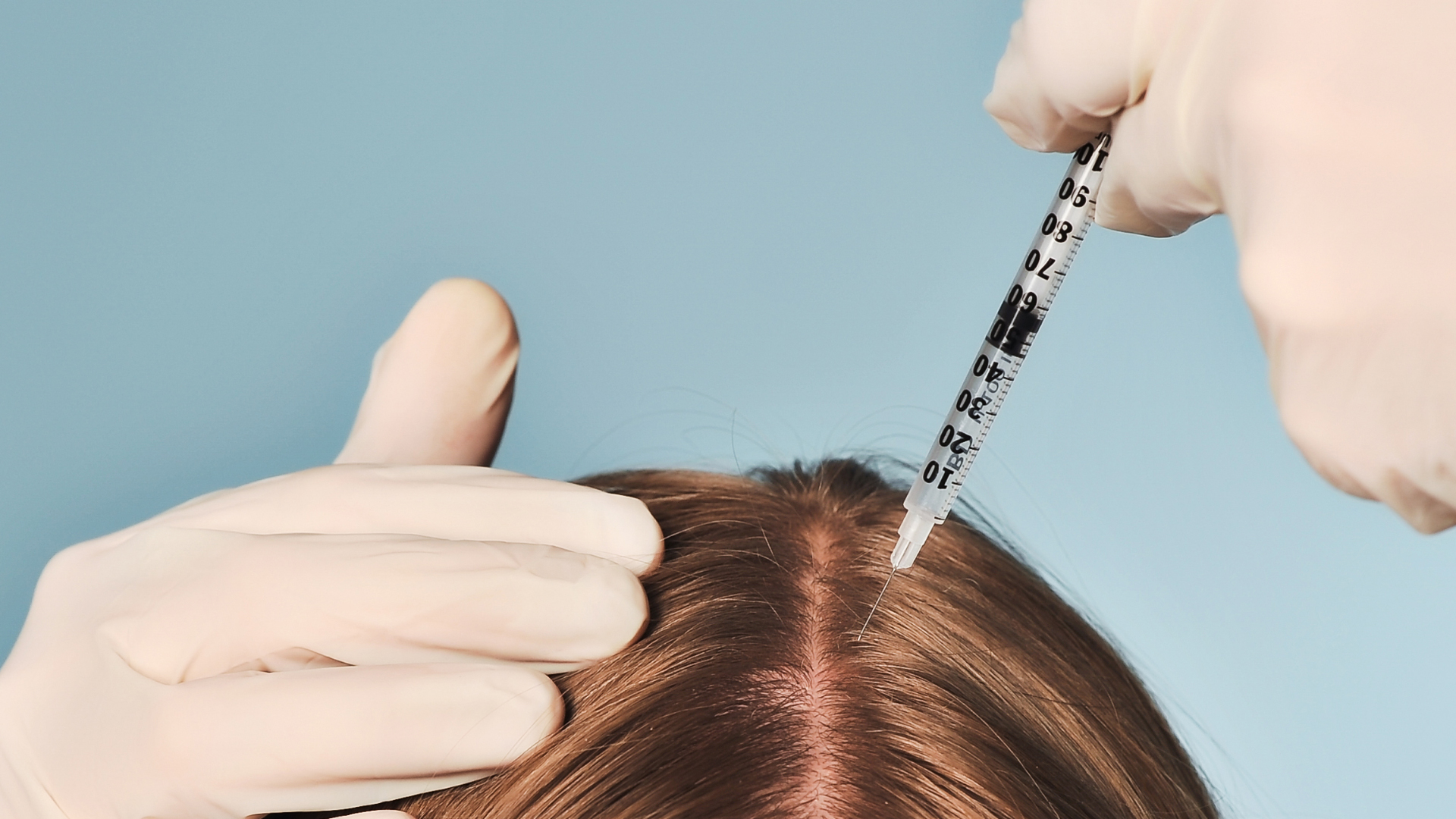
Hair transplants are generally a safe and effective solution for hair loss, with success rates ranging from 90% to 95%, and many people considering Hair Transplant in Chennai choose this option due to experienced surgeons and modern techniques. However, in rare cases, patients may experience unsatisfactory results following either FUE or FUT procedures. Common issues include poor hair density, inadequate growth, improper hair angles, continued hair loss, or visible scarring at the donor site. Fortunately, several corrective options exist for reversing or repairing a failed transplant.
Why Hair Transplants Sometimes Fail
Several factors can contribute to hair transplant failure:
- Graft rejection: Although rare, the body may fail to accept transplanted follicles, often due to autoimmune conditions such as alopecia areata or lichen planopilaris. These conditions can damage hair follicles, leading to temporary or permanent hair loss.
- Patient ineligibility: Ideal candidates are generally under 65, have a healthy donor area, and have stabilized hair loss. Excessive post-transplant hair loss can compromise the overall appearance of the procedure.
- Poor donor hair quality: The success of a transplant heavily depends on a thick, healthy donor area. Insufficient or weak follicles may lead to an unsatisfactory result.
- Inadequate aftercare: Proper post-transplant care is essential for graft survival. Neglecting aftercare instructions, such as gentle washing or avoiding friction, can negatively affect growth.
- Inexperienced surgeons or clinics: Unskilled practitioners may implant follicles incorrectly or over-harvest donor hair, resulting in poor outcomes. Unsanitary conditions can also increase the risk of infection.
How to Identify a Failed Hair Transplant
Signs of a problematic transplant include:
- Excessive scarring at the donor or recipient site
- Hair growing in unnatural directions
- Visible infection, swelling, or redness
- Poor follicle density or slow growth
- An unnatural-looking hairline
It is important to be patient, as it can take 9–12 months to fully evaluate the results of a transplant.
Corrective Options for a Failed Hair Transplant
- Second hair transplant: Often, a follow-up procedure can improve density and correct coverage in areas with inadequate growth. Surgeons first assess eligibility before proceeding.
- Hairline or follicle correction: If the hairline appears unnatural, FUE or FUT can reposition or replace poorly implanted follicles.
- Density improvement: Additional grafts can be implanted using FUE or FUT to increase hair thickness in sparse areas.
- Scalp micropigmentation: Also called a hair tattoo, this technique adds pigment to the scalp to simulate hair follicles, effectively disguising thinning areas or scars.
- Wide scar repair: Broad FUT scars can be camouflaged by combining FUE with micropigmentation, blending scars with existing hair.
If you are unhappy with your hair transplant results, consulting a skilled and experienced surgeon is crucial. A professional can assess your scalp, identify issues, and recommend the most suitable corrective approach. With the right strategy, even a poorly executed transplant can be repaired, restoring natural-looking hair and improving overall confidence.